Inward Remittance in India 2026 - Explained
If you sell products or services internationally, you encounter inward remittance — a critical concept with serious legal, compliance, and operational implications.
Understanding inward remittance is essential not just for finance and accounting teams, but also for product, growth, and payments teams. Misunderstanding it can slow down settlements, trigger regulatory holds, or create reconciliation bottlenecks.
This guide explains:
What inward remittance means in India
How it works technically
How it intersects with cross-border payments, forex, and compliance
The key documentation required
Common challenges and how to solve them
How xPay simplifies inward remittance for global merchants
Whether you want to optimize settlements or reduce delays, this guide gives you the clarity you need.
1) What is inward remittance?
Inward remittance is any money received into India from abroad.
For Indian businesses, inward remittance most commonly arises from:
Export of goods
Export of services (e.g., SaaS, consulting, tourism)
Royalties, licensing, or IP fees
Interest and dividend income
Foreign investment inflows
In simple terms:
If money enters your Indian bank account from a foreign source, that is inward remittance.
Inward remittance matters because it is regulated under FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) and must follow RBI rules for reporting, documentation, and compliance.
Understanding inward remittance is essential when collecting cross-border payments from international customers.
2) How inward remittance works: the technical flow
From transaction to INR in your bank account, inward remittance typically follows this technical sequence:
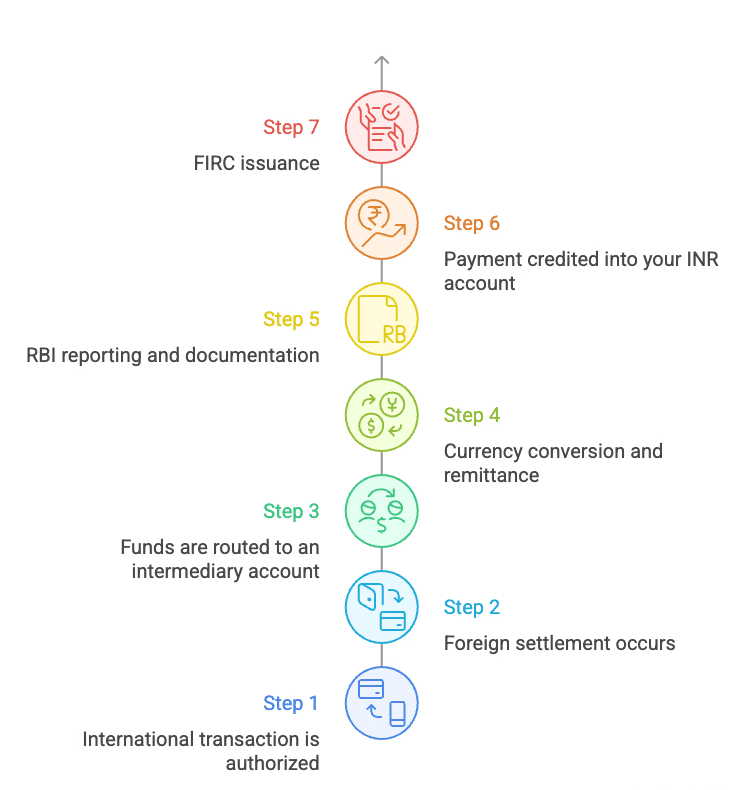
Step 1: International transaction is authorized
A foreign customer pays using a global payment method (card, wallet, alternate method).
Step 2: Foreign settlement occurs
The payment is captured and cleared in a foreign currency (USD, EUR, GBP, etc.) with the foreign issuing bank through a card network.
Step 3: Funds are routed to an intermediary account
This may be:
A foreign settlement account
A collection account in a foreign bank
Or a local acquiring partner’s account
This depends on your payment provider’s architecture.
Step 4: Currency conversion and remittance
The foreign funds are converted into Indian Rupees (INR) and remitted into an Indian bank account.
This remittance must be done via:
Regulated AD1 banking channels
Or through permitted Payment Aggregator – Cross Border (PA-CB) channels
Step 5: RBI reporting and documentation
The remitting bank or payment provider files requisite returns with RBI, reports the inward remittance, and ensures compliance with FEMA.
Step 6: Payment credited into your INR account
The converted INR lands in your nominated Indian bank account.
Step 7: FIRC issuance
A Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) is generated as a compliance proof of the inward remittance.
3) Regulations that govern inward remittance in India
Inward remittances in India are governed primarily by:
a) FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act)
FEMA regulates all foreign exchange in and out of India. Any foreign inflow must:
Be reported to RBI
Have valid documentation
Be linked to a permissible transaction type
b) RBI reporting requirements
Banks and payment providers must:
Report inward remittances on time
Use appropriate RBI return codes
Ensure purpose codes match the underlying transaction
c) Know Your Customer (KYC) guidelines
KYC applies not just to the merchant but also to the nature of the transaction.
This is why inward remittance is not just a banking term — it’s a regulatory control point that affects compliance, finance, and settlement speed.
4) Key compliance documents: FIRCs, purpose codes, and more
Compliance documentation ensures inward remittance is reportable, traceable, and auditable.
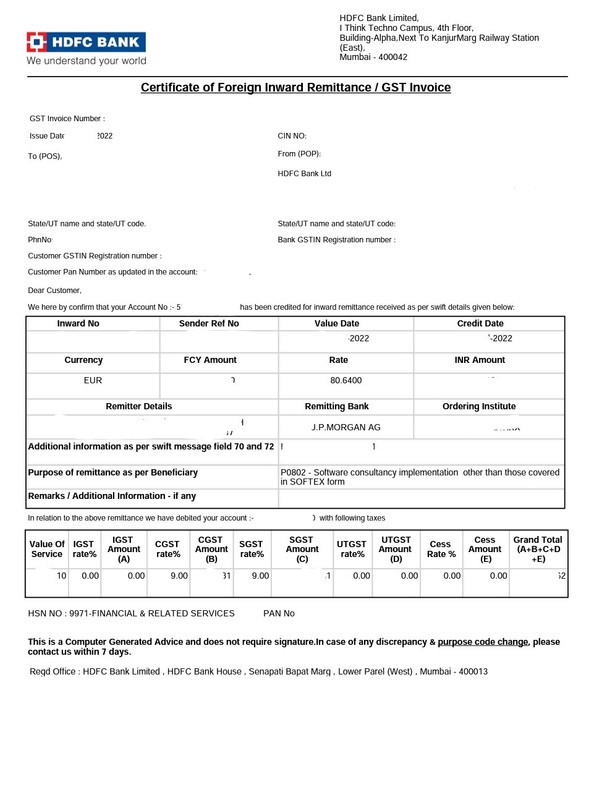
Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC)
A FIRC is issued by a bank or payment provider after inward remittance is credited and is used for:
GST compliance and exemptions
Accounting and audits
Proof of export earnings
Purpose code
A purpose code categorizes the transaction (e.g., export of software services, merchandise sales). It must:
Match the nature of the contract
Align with RBI and banking requirements
Contract or invoice
Export contracts or customer invoices support the purpose code and inbound remittance.
5) Why inward remittance matters for Indian exporters
For Indian exporters, inward remittance affects:
Cash flow timing
Tax compliance
GST filings
Accounting accuracy
Forex planning
Bank reconciliation
If inward remittances are delayed, incorrect purpose coded, or missing FIRCs, merchants face:
Blocked settlements
Additional banking queries
Audit risk
Manual reconciliation headaches
6) Common challenges with inward remittance
a) Incorrect purpose codes
Mismatch between contract and payment metadata leads to rejects or RBI queries.
b) Delayed FIRCs
Late FIRCs slow down reconciliation and tax compliance.
c) Settlement mismatches
When the remittance does not match the invoice value, reconciliation becomes manual and error-prone.
d) Unsupported payment methods
Some foreign payments cannot be remitted directly without special channels.
e) Split settlements and multi-currency complexity
If you have multi-currency accounts, matching remittances to invoices can be complex.
7) How xPay’s flow simplifies inward remittance
xPay is designed specifically for Indian businesses selling globally. Our infrastructure simplifies inward remittance by aligning technology, compliance, and banking rails.
Local acquiring for predictable settlement
xPay operates as a local Collection Agent, partnering with licensed processors and banks to collect international payments locally and then remit them to India.
This reduces:
Settlement delays
FX leakage
Cross-border bottlenecks
Regulated remittance into India
Funds are moved into India through:
AD1 banking channels
Permitted PA-CB providers
This ensures every inward remittance follows RBI’s compliance path.
Purpose code automation
xPay engineers purpose codes consistently at the transaction level, aligned with:
Vendor contracts
Export documentation
This dramatically reduces rejects and banking follow-ups.
Instant GST-compliant FIRCs
Unlike many settlement arrangements where FIRCs arrive days or weeks later, xPay’s rails:
Produce GST-compliant FIRCs at the moment of inward remittance
Reduce reconciliation delays
Support audit trails
Comprehensive reporting and dashboard
Merchants see:
Inward remittances credited
Purpose codes attached
FIRCs generated
Bank settlement matching
All in a single view.
FAQs
Q: What is a FIRC?
A: A Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate issued after inward remittance is credited. It is proof of foreign funds received, used for GST and audit.
Q: Do I need a purpose code?
A: Yes. Purpose codes are mandatory and must match the export nature.
Q: How long does inward remittance take?
A: With optimized rails like xPay’s, settlement and FIRC issuance can happen within hours.
Q: Can inward remittance impact tax compliance?
A: Yes. FIRCs and purpose codes are required paperwork for GST and accounting.






